Network & Remote Access
Serve CogDB graphs over HTTP, share publicly, and use the REST API.
CogDB includes built-in HTTP server capabilities for remote graph access and public sharing.
Serving a Graph
from cog.torque import Graph
g = Graph(graph_name="social")
g.put("alice", "knows", "bob")
g.put("bob", "knows", "charlie")
g.serve() # Start on port 8080Server Options
g.serve(
port=8080,
host="0.0.0.0",
blocking=False,
writable=False,
share=False # Enable public sharing
)Public Graph Sharing
Share your graph instantly with anyone on the internet using the CogDB relay service.
from cog.torque import Graph
g = Graph("my_graph")
g.put("alice", "follows", "bob")
# Share publicly via CogDB relay
g.serve(port=8080, share=True)
# Get the public URL
print(g.share_url()) # https://abc123.s.cogdb.ioThe graph server has the following interface that is served on the public URL (or local URL):
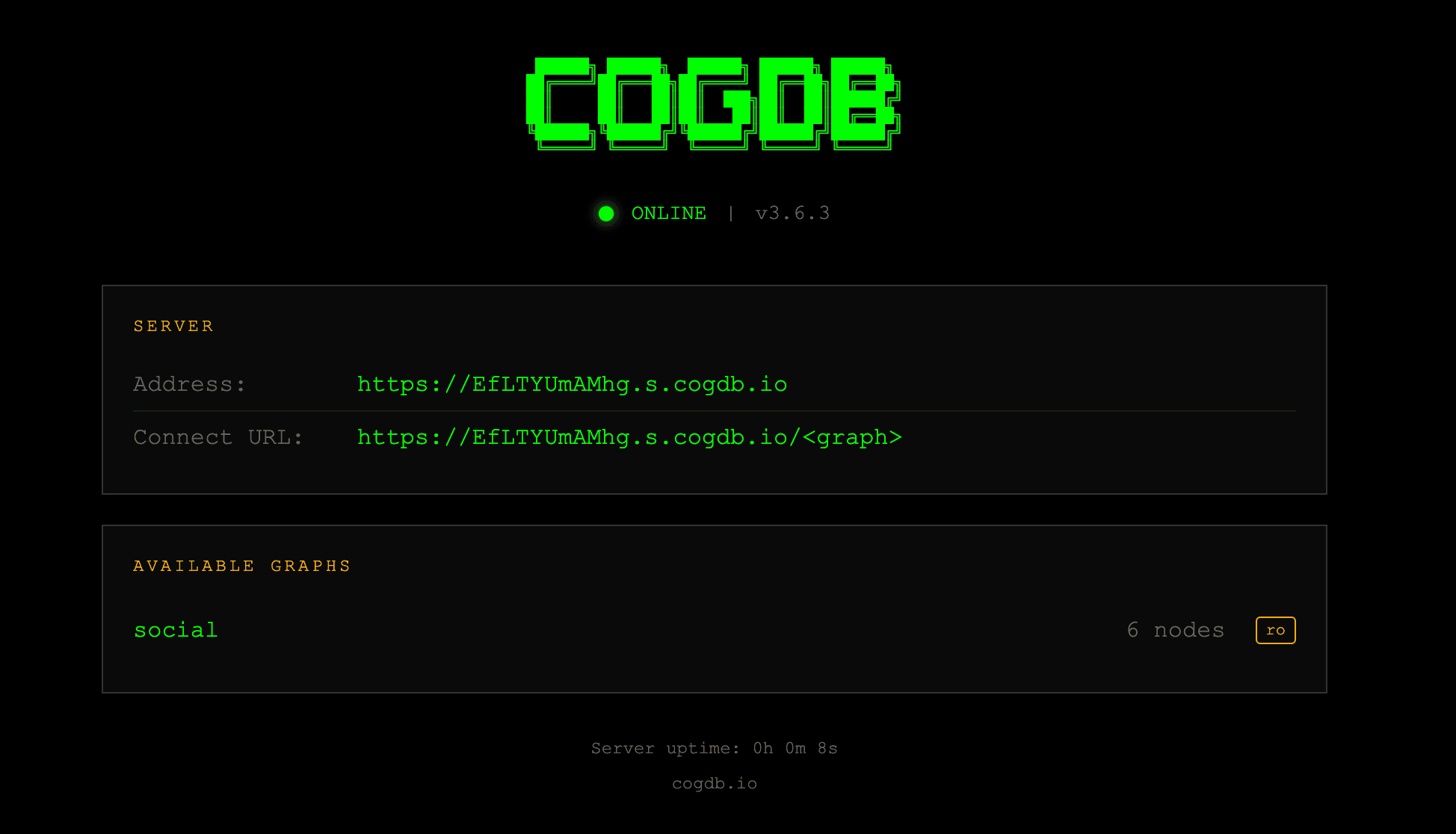
How It Works
- When you call
serve(share=True), CogDB establishes a secure WebSocket connection to the CogDB relay - The relay provides a unique public URL (e.g.,
https://abc123.s.cogdb.io/) that routes requests to your local graph - Your graph remains on your machine, the relay only forwards HTTP requests.
- Anyone with the URL to the public graph can query it (or write to it if
writable=True).
Public links are accessible to anyone. Only share URLs for graphs you intend to make public.
Use writable=True carefully! By default, shared graphs are read-only.
The server is intended for use in trusted networks. For production, add authentication via a reverse proxy.
You can also use third-party tunneling tools like ngrok, localtunnel, or Cloudflare Tunnel to expose your local graph server to the internet.
Configuration
The relay URL is configured in cog/config.py:
RELAY_URL = "wss://s.cogdb.io/register"Set RELAY_URL = None to disable sharing entirely.
Multiple Graphs
g1 = Graph(graph_name="users")
g2 = Graph(graph_name="products")
g1.serve(port=8080)
g2.serve(port=8080)
# http://localhost:8080/users/
# http://localhost:8080/products/Stopping
g.stop()
# Or stop all:
from cog.server import stop_server
stop_server(8080)Connecting Remotely
from cog.torque import Graph
remote = Graph.connect("http://192.168.1.5:8080/social")
result = remote.v("alice").out("knows").all()
# {'result': [{'id': 'bob'}]}REST API
| Method | Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | / | List all graphs |
| GET | /{graph}/stats | JSON statistics |
| POST | /{graph}/query | Execute query |
| POST | /{graph}/mutate | Write operations |
Query API
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/social/query \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"q": "v(\"alice\").out(\"knows\").all()"}'Stats API
curl http://localhost:8080/social/statsMutate API
Requires writable=True.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/social/mutate \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"op": "put", "args": ["charlie", "knows", "diana"]}'Security
The server is for trusted networks. For production, add authentication via a reverse proxy.
Built-in protections:
- Method whitelisting
- Dunder blocking
- Read-only by default
- Restricted eval